We are pleased to announce that our paper, “Accelerating Singular Spectrum Transformation for Scalable Change Point Detection,” by Lucas Weber and Richard Lenz, has been accepted for publication in IEEE Access (Open Access – Freely available: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3640386).
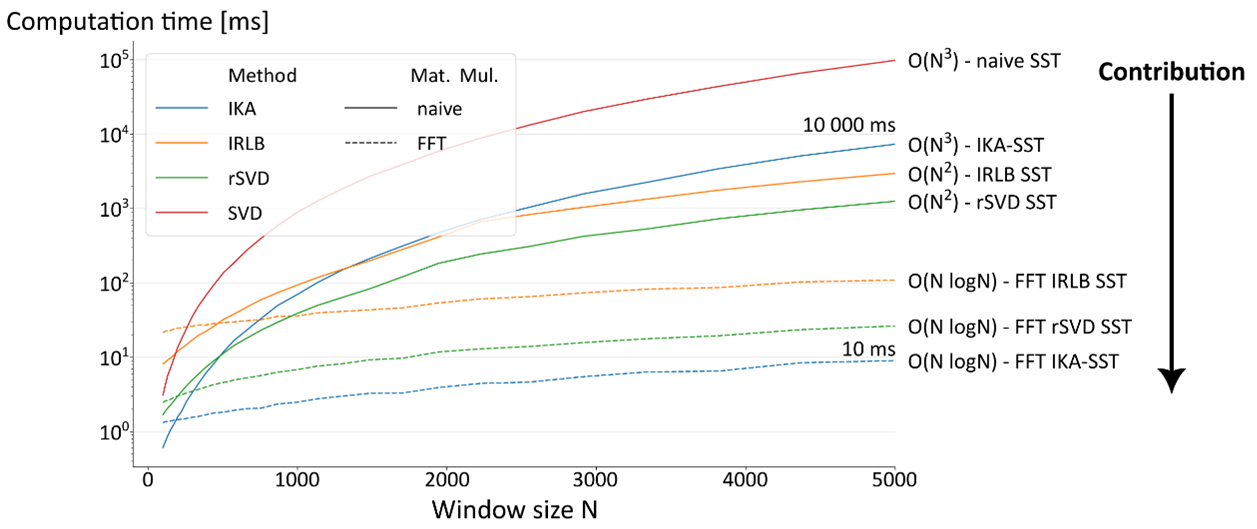
In short, the paper accelerates a common change point detection (CPD) algorithm (SST) by significantly reducing its computational complexity. In some applications, the SST is now 100x to 1000x faster, turning runs that previously took hours into minutes (and, in one case study, 22 hours into 22 minutes).
If you want to test our algorithm, we released reference implementations and experiment code, and provide a pip-installable package (changepoynt, https://github.com/Lucew/changepoynt) to make the improved methods easy to integrate into practical CPD pipelines.
Singular Spectrum Transformation (SST) is a widely used technique for change-point detection in time series, but its practical use is often limited by the quickly increasing runtime as the window size increases. In this work, we show how to make SST-based scoring scalable by combining randomized matrix decompositions (rSVD) with a fast Hankel matrix product that exploits FFTs.
This reduces the computational complexity of both SST and its variant, IKA-SST, from cubic (O(N³)) to log-linear time (roughly O(N log N)), while also cutting memory requirements from quadratic to linear.
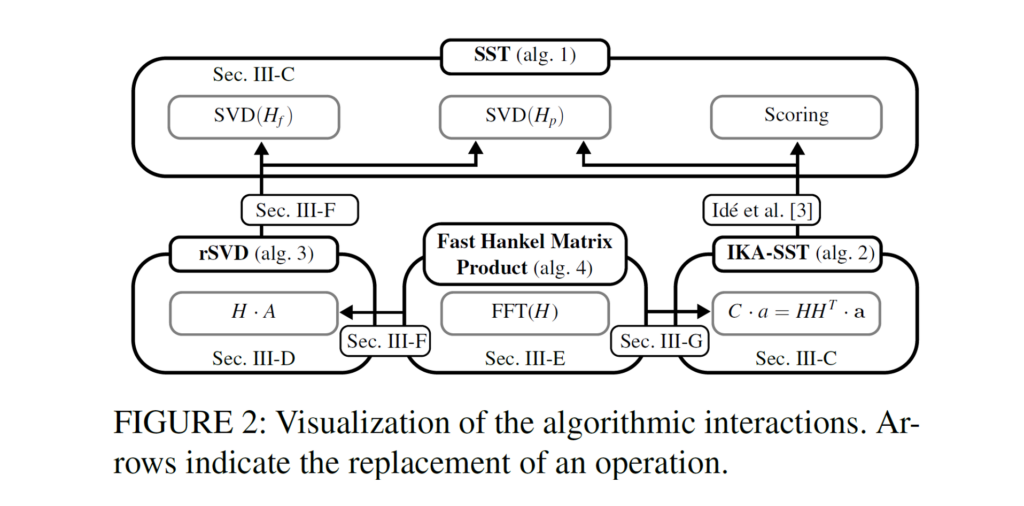
Beyond the algorithmic speedups, the paper also provides a thorough error analysis: by deriving an explicit bound, arguing that the approximation error remains small in the CPD setting.
This work was supported by Siemens Energy AG in the context of Project DARTS. We also appreciate the support of the Open Access publication fund of the Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU Publikationsfond).